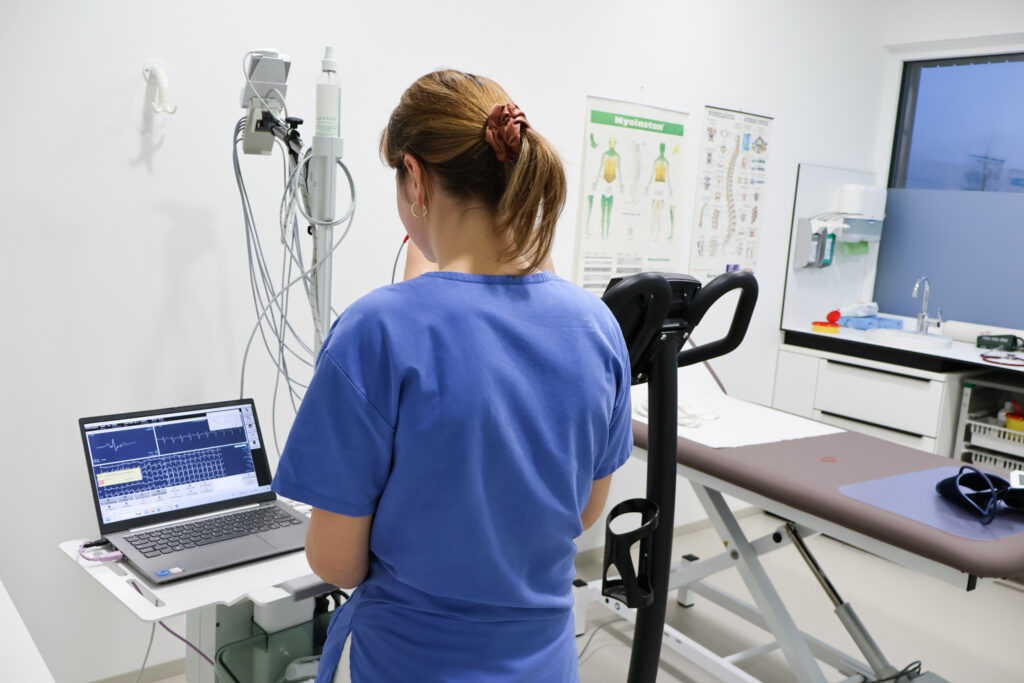
Ergometry is a procedure that measures your physical performance by observing certain bodily functions, including the electrocardiogram (ECG). It is also known as exercise ECG. In addition to its use in sports medicine, ergometry is mainly used in cardiology and pulmonology to assess exercise-induced changes in heart and lung activity. No special preparation is usually required, but ergometry should not be performed on an empty stomach.
The importance of ergometry in cardiological diagnostics
The exercise ECG is an important part of cardiological diagnostics. This procedure examines the heart’s response to controlled physical exertion in order to assess heart disease and its severity.
During ergometry, you will be exercised on a treadmill or cycle ergometer, with the intensity of the exercise being gradually increased. At the same time, the electrical signals from your heart are recorded using an ECG. The purpose of this examination is to detect changes in the ECG pattern during physical exertion that could indicate insufficient oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
When is this performance test carried out?
Ergometry is often used to diagnose coronary heart disease (CHD), as this disease typically leads to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, especially during exercise. By observing ECG changes such as ST segment deviations, doctors can draw conclusions about the extent of the circulatory disorder and make appropriate treatment recommendations.
In addition, this test can also be used to monitor your heart function. For example, if you already suffer from heart disease, to assess the effectiveness of medication or the need for interventional therapy.
The exercise ECG is a safe and cost-effective method of obtaining important information about your heart health. It enables doctors to identify individual risk factors, assess the prognosis and create a customized treatment plan for you. Regular stress tests can also detect changes in the course of the disease at an early stage and treat them accordingly.